Once the role and functions of the financial system have been defined, the next logical step is to know the structure of the financial system, as well as the purpose of the institutions that make part of it:
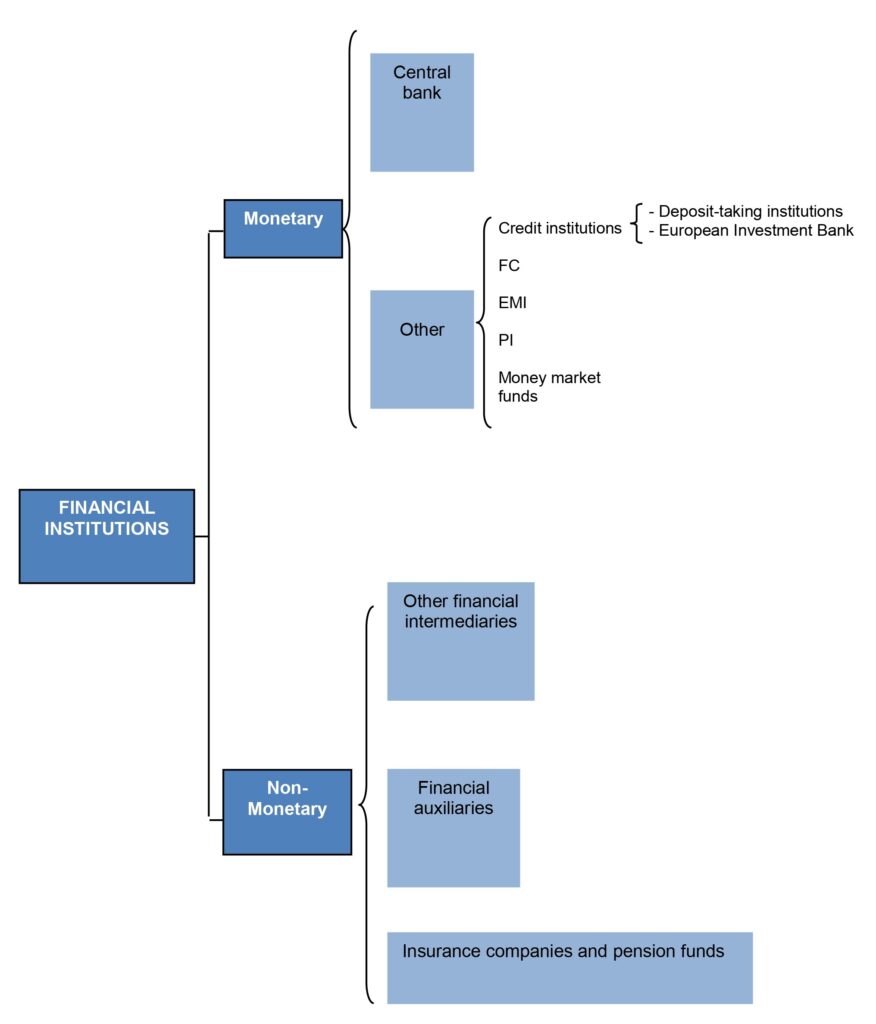
In a first approximation, the financial system is made up of the following types of entities:
- Central banks.
- Credit institutions.
- Finance companies (FC).
- Electronic money institutions (EMI).
- Payment institutions (PI).
- Money market funds.
- Other financial intermediaries.
- Financial auxiliaries.
- Insurance companies and pension funds.
- Regulatory bodies.
The Central Bank is in charge of:
- Setting the main lines and execute the monetary and exchange policies.
- Issuing legal tender bills and coins, putting cash into circulation.
- Carrying out foreign exchange transactions, and owning and managing official reserves.
- Promoting the proper functioning of the payment system.
- Fostering the proper functioning and stability of the financial system.
With regard to credit institutions, its main function is to raise funds from the public through various forms, with the obligation of refund, in order to allocate them to granting loans. They are made up of the following institutions:
- Deposit-taking institutions:
Deposit-taking institutions have the normal and usual activity of receiving funds from the public, assuming the commitment of their return, using them to grant loans and similar transactions.
This type of institution has reserved by law the exclusivity of the activity of raising funds directly from the public through deposits.
In the event that any of these institutions is declared bankrupt, depositors may resort to the Deposit Guarantee Fund.
- European Investment Bank (EIB)
The EIB (European Investment Bank) is an entity jointly owned by the EU countries whose objectives are to boost the growth and employment potential of the Eurozone, support measures to mitigate climate change and promote EU policies in other countries.
It secures its funding from the capital markets and offers three main types of products and services:
- Loans: To clients of all kinds to support growth and employment.
- Combined financing: Allows access to joint financing with other investments.
- Advice and technical assistance.
It offers directly its loans when the amount exceeds 25 million euros or through credit facilities in financial institutions for smaller amounts.
For their part, Finance companies carry out the following categories of transactions:
- Granting of loans and credit facilities.
- Recourse and non-recourse factoring, and the complementary activities of that business.
- Leasing or finance lease.
- Granting of guarantees and sureties, and underwriting of similar commitments.
- Granting of reverse mortgages.
- Rest of accessory activities that are necessary for the performance of the previous ones, in the terms that are foreseen in its bylaws.
As for the Electronic money institutions, it should be noted that they are dedicated to the issuance of electronic money admitted as a means of payment by companies other than the issuing institution. In a very simplified way, what these institutions do is to transform current money into electronic or private virtual money.
Finally, there are other types of financial intermediaries, such as:
- Payment institutions: Provide and execute certain payment services such as transfer, direct debits, and card payments.
- Undertakings for collective investment in transferable securities (UCITS): Investment companies and funds whose purpose is to raise funds for investing them in transferable securities and other financial assets, and in which the return of investors depends on the collective performance.
- Dealers: Intermediaries legally authorized to operate in the securities markets on behalf of others and on their own behalf.
- Asset securitization SPV (special purpose vehicle): Separate assets, without their own legal personality, whose assets are made up of financial assets (for example, loans from banks) or other rights.
- Venture capital companies and funds: Financial intermediaries that channel capital to small and medium-sized companies, by taking shareholdings in their capital stock, generally on a minority and temporary basis.
- Real estate collective investment undertakings: Investment companies and funds whose purpose is to raise funds in order to invest them in real estate for leasing purposes.
- Mutual guarantee and counter-guarantee companies: Companies specialized in granting guarantees to their partners, aimed at getting improvements in the financial conditions in their credit transactions.
On the other hand, Financial auxiliaries are institutions whose work is aimed at facilitating or complementing the operation of financial intermediaries. Among these, the approved appraisal companies and rating agencies occupy a prominent place.
- Approved appraisal companies: Entities in charge of certifying the value of real estate for financial institutions that grant mortgage loans.
- Rating agencies: Independent entities whose purpose is to rate the issues of certain financial assets with respect to the capacity of their issuers to meet the payment of their regular returns and the repayment of their capital.
Following with the defined diagram, the Insurance companies are in charge of covering the risks to which goods or people are exposed. In exchange for the payment of an amount (which is called a premium), the insurance company will pay the agreed amount (compensation) in the event of a certain event (claim), the risk of which is the object of insurance coverage.
The Pension funds are assets constituted with the contributions (and their returns) of the pension plan or plans attached to it. The pension plan regulates how contributions are made and how they are invested, in order to build up a set of assets with which to pay benefits to beneficiaries when the planned contingencies occur (retirement, death, disability, dependency).
Finally, a FAC (Financial Advisory Company) is a type of investment services company, established as a natural or legal person, which is authorized only to provide investment advice: Individualized recommendations to a client, based on their personal circumstances and with respect to one or more transactions related to specific financial instruments.
Along with financial institutions we can find the financial markets, which are those where financial instruments are traded, allowing their exchange. The following diagram shows the main financial markets:
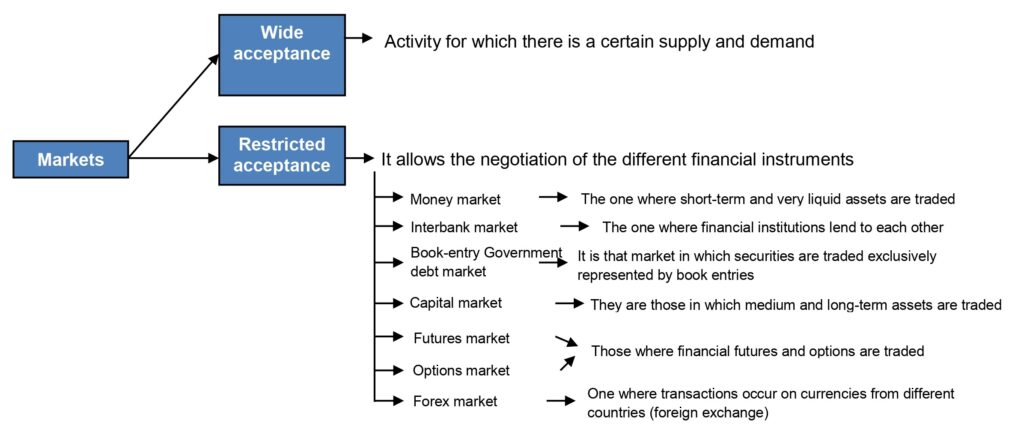
The main financial markets are the following:
- Money Market: It is the one where low-risk assets are traded wholesale, generally with short-term and highly-liquid maturities.
- Interbank Market: The one in which financial institutions lend and borrow money from each other, thus regulating their liquidity surplus or deficit.
- Government Debt Market: These are government debt markets in which securities issued by the State and other Public Governments are traded.
- Capital Market: Those markets in which the financing demanded is medium or long term. These markets can be classified according to different criteria:
- Depending on the assets that are traded in them:
- Securities market, whether debt or equity markets.
- Long-term credit market.
- Depending on its structure:
- Organized market: That official and recognized market that is regulated and supervised.
- OTC Market (“over the counter”): Those markets where the negotiation is carried out directly between the interested parties.
- Depending on the moment in time:
- Primary or issuance market: The one where the issued securities are traded for the first time.
- Secondary market: Place where successive sales of the securities already issued in the primary market take place.
- Depending on the assets that are traded in them:
- Futures and Options Market: Those markets where the so-called “financial derivatives” are traded. A futures contract consists of an agreement whereby two persons (natural or legal) agree to sell and buy, respectively, an asset, called the underlying asset, at a price and at a future date according to the conditions set in advance by both parts. For its part, the term option refers to an agreement by which the buyer is granted, in exchange for the payment of a price (premium), the right (not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a price (exercise price or “strike”) and at a future date, according to the conditions set in advance by both parties.
- Foreign Exchange Market: Are those in which purchase and sale transactions take place on the currencies of different countries (foreign exchange).
The supervisory bodies are institutions that operate in the financial system whose main functions are to regulate and control the actions of the economic agents that take part in the financial system, as well as to ensure that the market they regulate functions correctly and efficiently. The main regulatory bodies are listed in the following diagram:
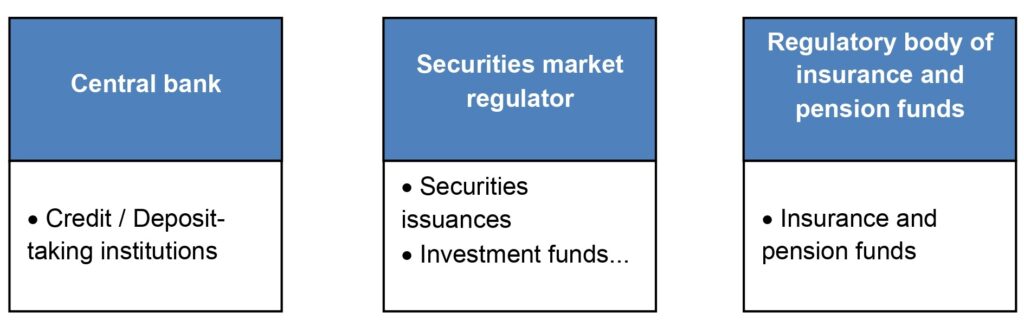
In this sense, within the regulatory bodies the following can be found:
- Central bank: Supervises the solvency and compliance with the regulations of credit institutions, other institutions and financial markets.
- Securities market regulator: Supervises the issuance of securities in the markets and controls the operation of investment funds. This regulator is called the “Comisión Nacional del Mercado de Valores” in Spain and the “Securities and Exchange Commission” in the United States.
- Regulatory body for insurance and pension funds: Its main task is to ensure that insurance companies and pension funds comply with the established regulations, in order to guarantee the proper functioning of the insurance and pension funds market.















