The needs that may arise for a person in the financial field are multiple. Obviously, the needs that arise in practice present a series of specific nuances, that must be taken into account, but, in a first approximation, most can fit into the following typology:
- To save.
- To make payments.
- To have liquidity at hand.
- To make a currency exchange transaction.
- To get resources on credit.
- To secure a guarantee against third parties.
- To cover certain risky situations.
The different categories of financial products can be determined according to the needs they meet, as established in the following diagram:
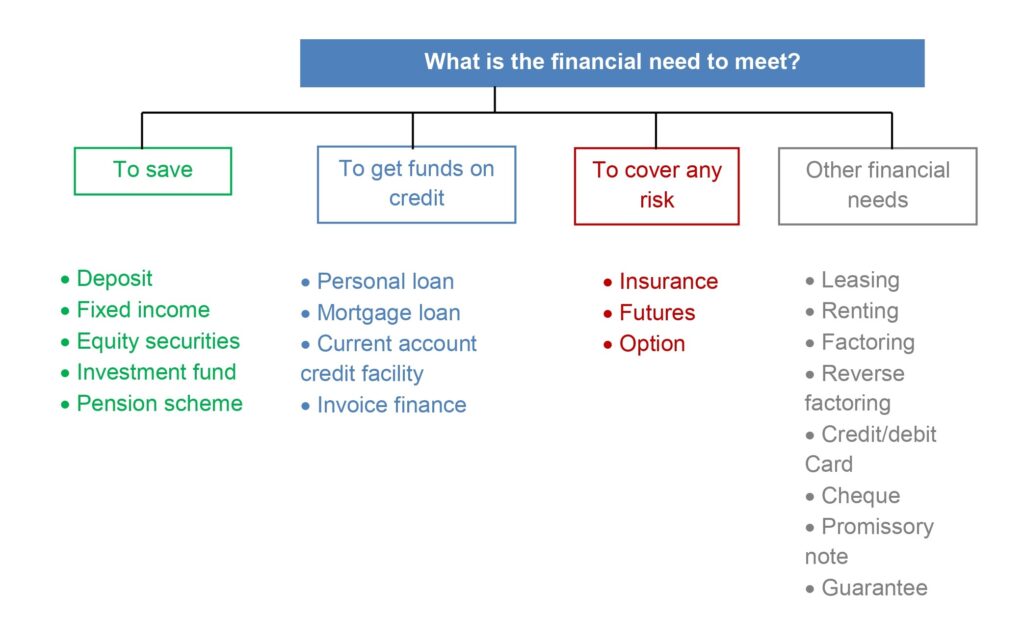
- Savings/Investment products: Products that allow savings to be made, either in search of return or simply as a means of depositing funds. Products such as deposits, fixed income and equity instruments or investment funds can be included in this category.
- Loans: They make possible to get resources on credit, allowing the borrower to carry out a spending project, whether for consumption or investment purposes.
- Insurance: They are intended to cover a certain risk. Thus, insurance can be considered as a protection system for the person and their assets against various contingencies that threaten their physical integrity, health, financial position or properties. To this end, the policyholder must pay a premium in exchange for coverage.
- Other financial products: This category includes complementary products to those indicated above, which help users to work properly or allow specific needs to be met. These are products such as means of payment, guarantees or financial derivatives products.















